Learn about 4c's of diamonds
Why Cut Is so Much Important In diamonds
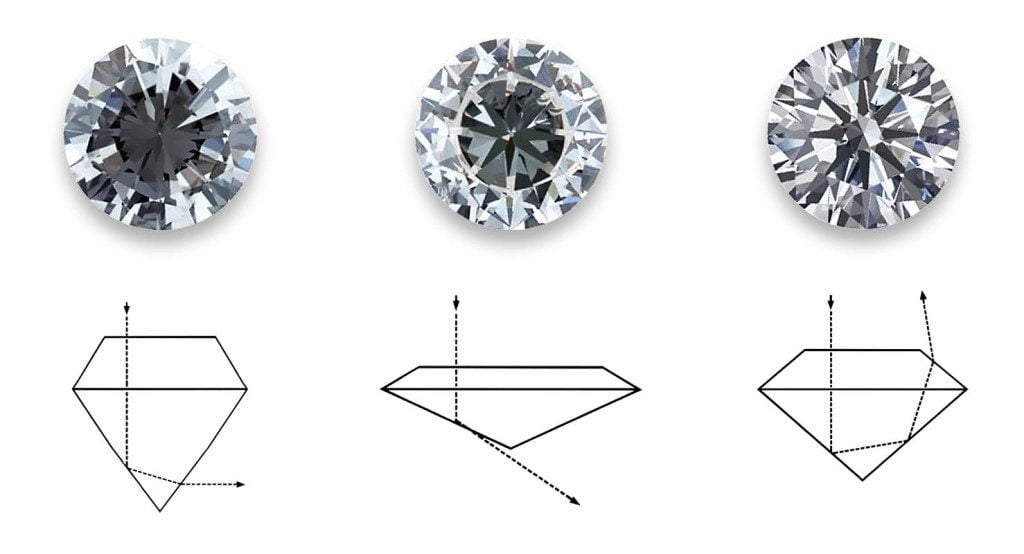
When it comes to estimated cut grades for princess, cushion, and emerald diamonds, understanding how these assessments are made is key to choosing a stunning gemstone. Unlike round diamonds, which have official cut grades, these fancy shapes often do not receive formal cut grading on their certificates. However, experts provide estimated cut grades for princess, cushion, and emerald diamonds by analyzing parameters such as depth, table size, and facet arrangement to predict their light performance.
A well-estimated cut grade ensures that your diamond will reflect light beautifully, maximizing sparkle and brilliance. This process considers the unique proportions of each shape, recognizing that the traditional grading system primarily focuses on rounds. By paying attention to these expert estimates, buyers can confidently select diamonds with superior cut quality, even for less common shapes, ensuring their jewellery radiates exceptional fire and brilliance.

Diamond Cut
The diamond cut plays a crucial role in the brilliance of a diamond, influencing how light reflects within the stone beyond just the diamond shape. An ideal diamond cut maximizes sparkle and can even make the stone appear larger than its actual carat size. In contrast, a poorly cut diamond appearance can look dull and lifeless, regardless of its color or clarity.
Understanding the cut of the diamond and light reflection is essential for selecting a diamond with exceptional beauty. Ultimately, diamond brilliance regardless of color and clarity depends heavily on the quality of its cut, making it one of the most important factors to consider.
Ideal cut diamonds
Our elegant selection of ideal cut diamonds includes stunning round brilliant diamonds and exquisite princess shape diamonds, each crafted to maximize light performance. Whether you’re selecting ideal cut diamonds that dazzle from every angle or searching for radiant ideal cut diamonds for unforgettable moments, precision cut techniques ensure every stone sparkles brilliantly.
These ideal cut diamonds for special moments are designed to enhance sparkle and fire, making your jewellery truly exceptional. Experience the beauty of maximizing diamond sparkle with precision cut techniques when choosing your perfect diamond.
Hearts and Arrows Diamond
The Hearts and Arrows diamond is renowned among precision cut diamonds for its exceptional diamond symmetry and flawless craftsmanship. When viewed from the diamond pavilion side, this unique cut reveals the iconic Hearts and Arrows diamond pavilion view, showcasing a perfect pattern of hearts and arrows that symbolize impeccable precision. Our exclusive Hearts and Arrows diamond collection features stones that are not only stunning but also represent diamonds symbolizing love with perfect symmetry.
These luxury Hearts and Arrows diamonds symbolizing eternal love are crafted to dazzle from every angle, making them the perfect choice for those seeking brilliance and romance in one exquisite package. Discover the unmatched beauty and meaning behind these precision masterpieces today.

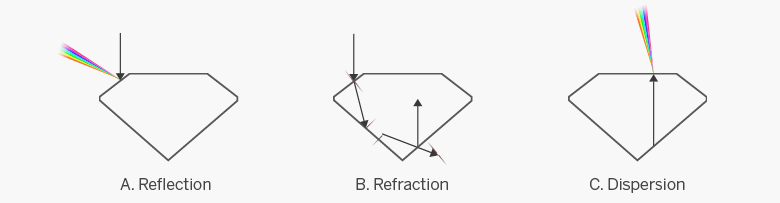
Understanding Brilliance, Dispersion & Scintillation
A diamond’s unforgettable sparkle comes from three main elements: brilliance, fire, and scintillation. Brilliance is the return of white light from the surface and inside of the diamond. Fire refers to the colorful flashes of light caused by dispersion, where white light splits into rainbow hues. Scintillation is the sparkle effect seen when the diamond moves. Together, these optical effects create the breathtaking shine that buyers love. Understanding what makes a diamond sparkle helps you choose a stone that truly stands out.
The Effects Of Light On A Diamond
Diamond brilliance is directly influenced by how well the diamond is cut. A precisely cut diamond redirects incoming light back through the top surface, creating a radiant, eye-catching sparkle. When the angles and proportions are ideal, the diamond traps light and reflects it in a way that maximizes brilliance. Poor cuts cause light to escape through the bottom or sides, reducing the stone’s shine. Understanding how diamond cut redirects light helps buyers choose diamonds with optimal brilliance and beauty.
Expert Tip
When selecting a diamond, understanding diamond cut grades is essential for maximizing both beauty and value. An Excellent cut diamond offers superior light performance and brilliance, while a Good cut diamond can be a smart choice for those on a budget, offering sparkle without sacrificing too much on visual appeal. When choosing between diamond cut grades, it’s important to consider how the cut impacts the diamond’s perceived size and light return. Experts recommend you avoid deep cut diamonds that look smaller than their actual carat weight. For budget-conscious buyers, value-focused diamond cuts that still shine brilliantly can be a great alternative. Discover the best diamond cut options for visual size and brilliance, especially when choosing the best diamond cut grade for engagement rings that truly stand out.
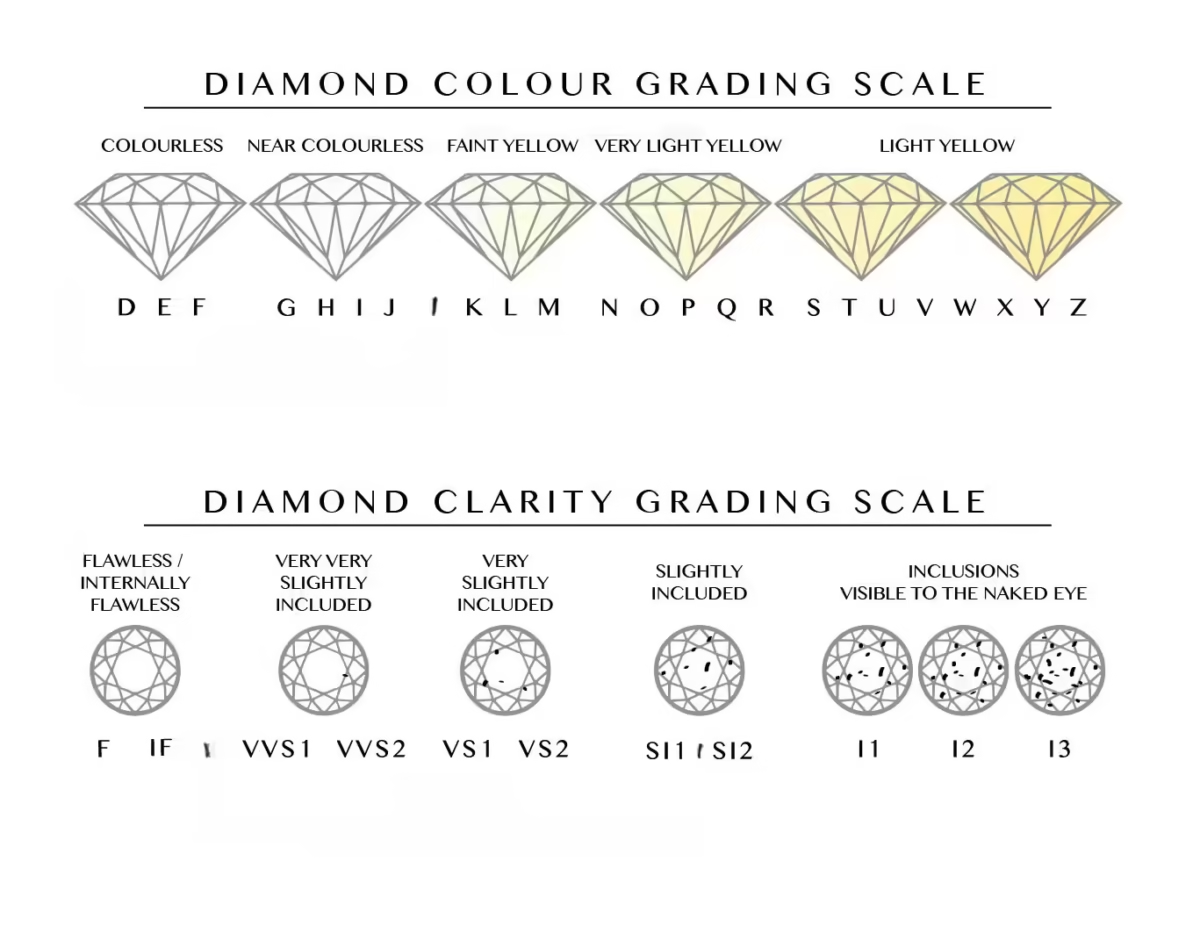
When it comes to selecting white diamonds, understanding the D to Z color scale is essential. This scale, adopted by the diamond industry, ranks diamonds from completely colorless (D) to light yellow or brown (Z).
The diamond color categories are broken down into five main groups: colorless, near colorless, faint, very light, and light. Among these, colorless diamonds, particularly those graded D and E, are the rarest and therefore command premium prices. The rarity and pricing of colorless diamonds (D, E) make them highly desirable for those seeking the purest brilliance.
However, most buyers benefit from a side-by-side diamond color comparison, where the subtle differences between grades like D and G become noticeable. This method helps in determining the best diamond color for the price, especially for those balancing budget with visual appeal. Diamond color grading can be complex, but understanding how color affects overall appearance is key.
The impact of budget and personal preference on color selection should not be underestimated – what might be a perfect choice for one may not suit another. Whether you’re buying for value or rarity, knowing the nuances of the diamond color categories ensures you choose a stone that truly reflects your expectations.
Diamond Color
Understanding the diamond color scale & grading is essential when selecting a stone that reflects your personal taste and budget. Diamonds are evaluated using the D to Z diamond color grading scale, where a colorless diamond (graded D-F) is the rarest and most valuable. As the scale progresses, a yellow tint in diamonds becomes more noticeable, often caused by trace amounts of nitrogen. Knowing how diamond color is graded helps buyers make informed decisions. This process occurs under precise conditions, including diamond color grading under controlled lighting, to ensure accuracy. A helpful technique involves comparing diamond colors side by side, which reveals subtle variations that may not be visible individually.
Our side-by-side diamond color grading guide for buyers emphasizes the difference in diamond hues from side profile, where color becomes more apparent than in the face-up vs side-view diamond color visibility comparison. When selecting the right diamond color for natural brilliance, consider that near-colorless diamonds offer an excellent balance of beauty and value. Whether you’re aiming for brilliance or budget-friendly elegance, understanding color grading ensures a confident purchase.
Colorless Diamonds (D-F):
Near Colorless Diamonds (G-J):
Near colourless diamonds often appear colourless to most buyers, especially when set in jewelry. However, a slight hint of colour in diamonds can be noticed when viewed from the side or face-down. Understanding this hidden color in near colourless diamonds revealed by side and face-down views is key to buying near colourless diamonds with optimal value and appearance. Despite these subtle hues, the value of near colourless diamonds remains exceptional, offering a perfect balance of beauty and affordability.
Faint Color Diamonds (K-M):
Faint colour diamonds showing subtle yellow or brown hues are often influenced by internal graining, a natural result of structural irregularities within the stone. These irregularities are mainly caused by nitrogen impurities that create the common yellow and brown tints seen in diamonds under the faint colour range.
When viewed from the face-up position, these trace colours may be visible, affecting the diamond’s overall appearance. Understanding how internal graining impacts the colour of faint diamonds helps buyers make informed decisions when selecting stones with delicate colour nuances.

EXPERT TIP 2
H graded diamonds offer an excellent balance between affordability and quality, often considered near colourless diamonds with minimal visible tint. These premium quality H graded diamonds without visible yellow tint provide great value for buyers seeking brilliance without the higher price tag of whiter grades. When comparing H graded diamonds to whiter color grades for value, it’s clear they deliver stunning sparkle and clarity for budget-conscious buyers.
EXPERT TIP 2
Choosing budget-conscious diamond buyers often means considering K and L diamonds on a GIA certificate, which offer acceptable diamond tint at a more affordable price. To enhance the appearance of these slightly tinted diamonds, experts recommend setting tinted diamonds in yellow or rose gold jewelry, which helps mask color and maximize brilliance without compromising on size or budget.
EXPERT TIP 1
When selecting colourless diamonds in the D to G diamond color range, buyers often find the difference between these grades barely visible to the untrained eye. Choosing diamonds within this range can offer significantly better diamond color value, making them an excellent choice for both the diamond investor and the diamond connoisseur seeking quality without overpaying.
EXPERT TIP 1
When choosing I and J diamond color grades, it’s crucial to opt for GIA certification for diamond color to ensure authenticity and meet your color expectations in diamonds. While these diamonds may appear face up white, slight yellow or brown tints in diamonds can be detected when viewed from multiple angles, making accurate assessment essential.
How to choose a clarity grade?
When selecting a diamond, expert advice for selecting diamonds with VS2 clarity or higher is essential to ensure you choose a stone free from visible inclusions and blemishes. Understanding how to balance diamond clarity and color for maximum value can help you find the perfect match, especially when considering diamonds in the D-F and G-I diamond colors. While SI clarity diamonds can offer great value, it’s always best to get a professional evaluation for SI clarity diamonds before purchase to avoid stones with distracting inclusions. By choosing clean diamonds without visible inclusions under the naked eye, you ensure both beauty and durability. This approach offers affordable diamond clarity options without compromising beauty, making it easier to invest wisely. Our experts provide tips for buying diamonds with minimal inclusions and blemishes, helping you make an informed decision. Ultimately, understanding diamond clarity grades for smart jewelry investment can guide you to the best value-focused clarity and color combinations that suit your budget and style.

The 4 Diamond Clarity Factors
Size
Visible flaws and noticeable inclusions can significantly impact the degree of purity in diamonds. Understanding how these characteristics affect diamond purity grades is essential to select a stone with optimal clarity and value.
Number
The degree of purity in a diamond is greatly influenced by the number of visible features it contains. Diamonds with fewer visible inclusions and minimal observable characteristics achieve a higher diamond purity grade, enhancing both their beauty and value.
Position
Internal diamond features located under the table or near the pavilion can significantly affect the diamond’s refraction and overall brilliance. The impact of inclusions near the diamond pavilion is especially critical because these flaws can interfere with light performance, reducing the perceived purity and sparkle of the stone. Understanding how internal diamond features influence the degree of purity helps buyers select diamonds with optimal clarity and visual appeal.
Nature
Understanding natural diamond inclusions and durability is essential when selecting a high-quality diamond. These diamond inclusions form naturally during the crystal’s growth and can significantly impact the gem’s strength and beauty. By learning about the types of diamond inclusions and their effects, you can choose a stone that maintains its lasting brilliance while offering optimal durability.
Diamond Clarity FAQ's
Why VVS Diamonds And VS Diamonds Are The Best Value
When selecting a diamond, many buyers ask “Are Flawless diamonds worth the price?” While Flawless (FL) and Internally Flawless (IF) diamonds are extremely rare and prestigious, opting for VVS or VS diamond clarity offers affordable brilliance with high clarity. These stones contain invisible inclusions that are not noticeable to the naked eye, making them an excellent choice for beauty and value.
Understanding diamond clarity for smart shopping ensures you don’t overpay for perfection that can’t be seen.
Diamond Clarity/Shape
Step-cut diamonds like the emerald cut and Asscher cut require higher diamond clarity due to their large, open facets that reveal even minor imperfections. Choosing a VVS or IF clarity grade ensures a flawless appearance, especially when aiming for maximum transparency. These high clarity diamonds for clean-cut sparkle are ideal for buyers seeking refined elegance without visible inclusions.
Understanding what clarity is best for emerald cut diamonds helps maintain both value and visual perfection.
Diamond Clarity/Size
Understanding fancy diamond color value is essential when comparing them to traditional colorless diamonds. These gems are graded on a unique color scale that highlights their rarity and beauty, making fancy color diamonds more valuable in many high-end jewelry collections.
The Diamond Clarity in the Certificate
When evaluating a diamond’s clarity, it’s essential to understand diamond clarity diagrams provided in GIA certificates. These diagrams help identify internal characteristics of a diamond, such as inclusions and blemishes, which can impact visual appeal and value. The visibility of diamond inclusions in different positions – whether at the center or near the edge – can affect how noticeable they are to the naked eye.
Learning how to interpret GIA diamond inclusion charts ensures you choose a stone with optimal brilliance and minimal visible flaws.
EXPERT TIP 1
When selecting a diamond with a VS1 grading or higher, it’s important to understand that magnification is needed to see impurities at this level. Choosing a VS1 or higher diamond is often a subjective decision focused on quality beyond the unaided eye. Larger diamonds with these higher clarity grades are much rarer, which results in higher pricing premiums and better potential as a long-term investment. Opting for diamonds in this category ensures both exceptional beauty and lasting value.
EXPERT TIP 2
SI1 diamonds often offer great value and can appear visually flawless to the naked eye, especially when the inclusions are small, light-colored, or scattered. While not technically “eye-clean” by strict grading standards, up to 20% of SI1 diamonds may look free of visible flaws without magnification. This makes them a popular choice for buyers seeking beauty without the premium price of higher clarity grades.
Understanding how inclusions affect appearance can help you select an SI1 diamond that sparkles brilliantly in everyday wear.
Carat Weight
The carat weight of a diamond is a crucial factor that directly affects its size and value. Understanding the origin of the word carat helps appreciate its historical significance, as it was named after carob seeds once used as a natural carat measurement tool. Today, diamond carat weight is measured with precision using modern techniques, but the unique history of diamond carat weight measurement remains an important part of choosing the perfect stone. Knowing how carat weight impacts diamond value and size can guide you to make an informed purchase.
Diamond Size and Diamond Carat Weight
Understanding the diamond carat weight vs face-up diameter is essential when selecting the perfect stone. While the carat weight measures the overall weight of a diamond, the visible size or face-up diameter increases at a slower rate. For example, a two-carat diamond will weigh twice as much as a one-carat but only appears about 30% larger in diameter. This distinction helps explain why larger diamonds are priced higher, as their carat weight significantly impacts value more than their visible size alone. Knowing this difference ensures you make a smart investment without compromising on appearance.
Which Carat Weight Is Right For You?
When selecting the ideal diamond engagement ring size visually, it’s important to prioritize the diamond cut and diameter over carat weight. A well-cut diamond with the right diameter can appear larger and more brilliant than a heavier stone with poor proportions. Understanding the difference between face-up diamond size versus carat weight helps buyers choose a ring that looks stunning while staying within budget. Focusing on diamond diameter vs carat for engagement rings ensures you get the best value and brilliance for your investment.
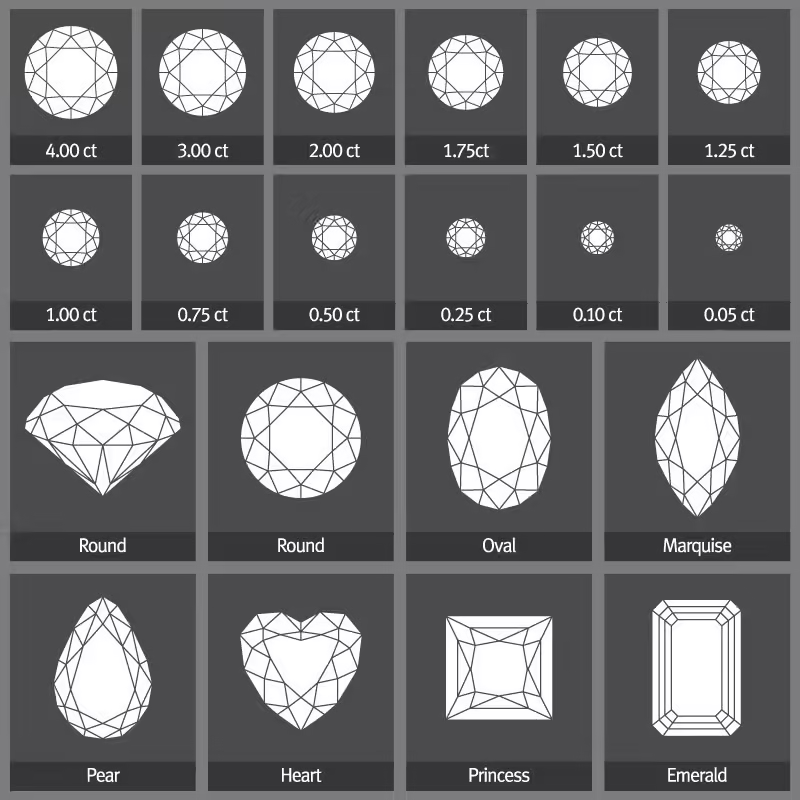
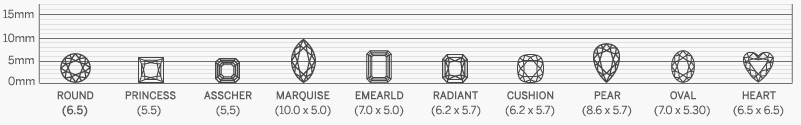
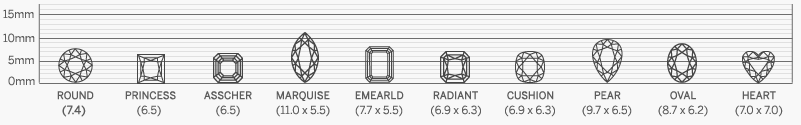
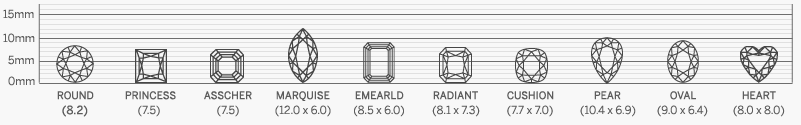
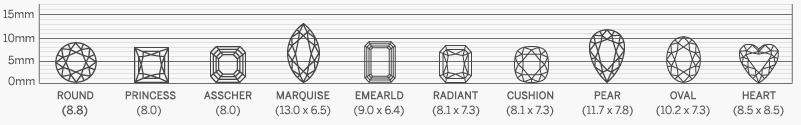

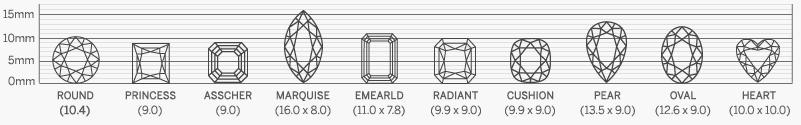
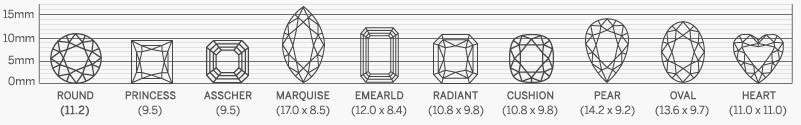
Diamond Shapes
Choosing the right diamond shape is essential when selecting the perfect stone, as each shape offers its own unique qualities. Our collection features certified high-quality diamonds for enthusiasts who appreciate both beauty and craftsmanship. Understanding the differences among unique diamond shapes and styles can help you make a confident decision. At Sunny Diamonds, we provide a comprehensive guide to diamond shapes and qualities to ensure you find the ideal match for your style and preferences.
Emerald Step Cut Diamond
When selecting Asscher cut diamond engagement rings with high clarity, it’s essential to consider how the step-cut facets and octagonal shape emphasize the diamond’s internal characteristics. Unlike brilliant cuts, Asscher cut diamonds reveal inclusions more easily, making clarity a crucial factor. Choosing a flawless or VVS Asscher diamond ensures a clean, transparent appearance that enhances its vintage charm and light performance.
Round Brilliant Cut Diamonds
For those seeking unmatched brilliance in their engagement ring, cone-shaped round diamonds for maximum sparkle are a timeless choice. The Round Brilliant cut is designed to reflect light beautifully through its 58 expertly arranged facets, enhancing its fire and brilliance. With precise crown and pavilion angles, these diamonds offer optimal visual impact, making them ideal for modern proposals. Choosing the best round brilliant diamond cut for engagement rings ensures a dazzling centerpiece that captures attention from every angle.
Cushion-Cut Diamonds
Known for their timeless elegance and historical roots, Vintage-inspired Cushion Cut engagement rings offer a perfect blend of antique craftsmanship and modern-day romance. With soft edges and deep facets, this cut echoes the charm of the Old Mine Cut while maintaining the brilliance of more contemporary shapes like the Oval Cut. Ideal for those who appreciate old-world beauty, these rings reflect the hand-cut artistry of the 19th century, capturing the warmth and sparkle once admired under candlelight.
Emerald-Cut Diamonds
Known for their exceptional emerald-cut diamond clarity, precision cut diamonds like the Emerald cut showcase a unique beauty defined by clean lines and subtle sparkle. While some may note emerald-cut diamonds with less brilliance compared to other shapes, their understated emerald-cut brilliance highlights the stone’s pure transparency and refined craftsmanship. Inspired by the origin of Emerald cut in gemstones, these refined step-cut diamonds with icy geometric lines are a perfect choice for luxury engagement rings with emerald-cut precision, offering timeless elegance and sophisticated style.
Heart Diamonds
Marquise-shaped diamonds have long been a staple among classic diamond engagement rings, celebrated for their elegant, boat-like silhouette. As a distinctive member of the fancy-cut stones family, they require careful attention to colour and clarity in diamonds to maximize their brilliance. The cutting process of Marquise-shaped diamonds shares similarities with the traditional Round-cut diamond cutting process, but with a unique focus on Marquise diamond carat weight maximization, elongating the stone to enhance its size and appeal. Today’s fancy-cut Marquise diamonds with minimal inclusions make stunning choices for those seeking a refined and timeless engagement ring style.
Oval Diamonds
Oval diamonds are a stunning variation of the Round Brilliant Cut, often referred to as modified Round Brilliant Cut diamonds due to their unique shape and facet arrangement. These Oval-cut diamonds offer the best of both worlds — the timeless sparkle of traditional rounds with an added elegance that creates the oval diamond shape illusion benefits, making fingers appear longer and more slender. Perfect for brides who want a distinctive yet classic look, oval diamonds for brides seeking unique yet classic cuts have become a popular choice. In fact, they are widely considered among the best diamond shapes for long, elegant fingers, enhancing grace and sophistication with every wear.
Pear Diamonds
Pear-shaped diamonds are a dazzling choice, expertly crafted with 58 facets diamond precision to maximize their unique sparkle. Blending the elegance of Round-cut diamonds with a distinctive silhouette, these stones deliver exceptional pear-shaped diamond brilliance and captivating round-shaped diamond light reflection. The facet design in pear-shaped diamonds allows for excellent pear-shaped diamond light performance, creating an enchanting play of light that rivals traditional cuts. For those seeking something special, unique pear-shaped diamond engagement rings offer a blend of classic beauty and individuality, with choosing the size and shape of pear-shaped diamonds being a personal journey reflecting one’s taste and style.
Heart Diamonds
Marquise-shaped diamonds have long been a staple among classic diamond engagement rings, celebrated for their elegant, boat-like silhouette. As a distinctive member of the fancy-cut stones family, they require careful attention to colour and clarity in diamonds to maximize their brilliance. The cutting process of Marquise-shaped diamonds shares similarities with the traditional Round-cut diamond cutting process, but with a unique focus on Marquise diamond carat weight maximization, elongating the stone to enhance its size and appeal. Today’s fancy-cut Marquise diamonds with minimal inclusions make stunning choices for those seeking a refined and timeless engagement ring style.
Princess-Cut Diamonds
Radiant Cut Diamonds
The Radiant-cut diamond is a brilliant fusion of two iconic diamond cutting styles—the Round brilliant cut and the Emerald cut—offering a truly unique Radiant-cut diamond style that stands out in the world of fine jewelry. First crafted by Henry Grossbard in 1977, the Radiant-cut diamond craftsmanship since 1977 reflects decades of innovation and artistry. These Radiant-cut diamonds captivate with their exceptional brilliance and a distinctive shape that blends the best features of its classic predecessors, making them a popular choice for those seeking something elegant yet different.

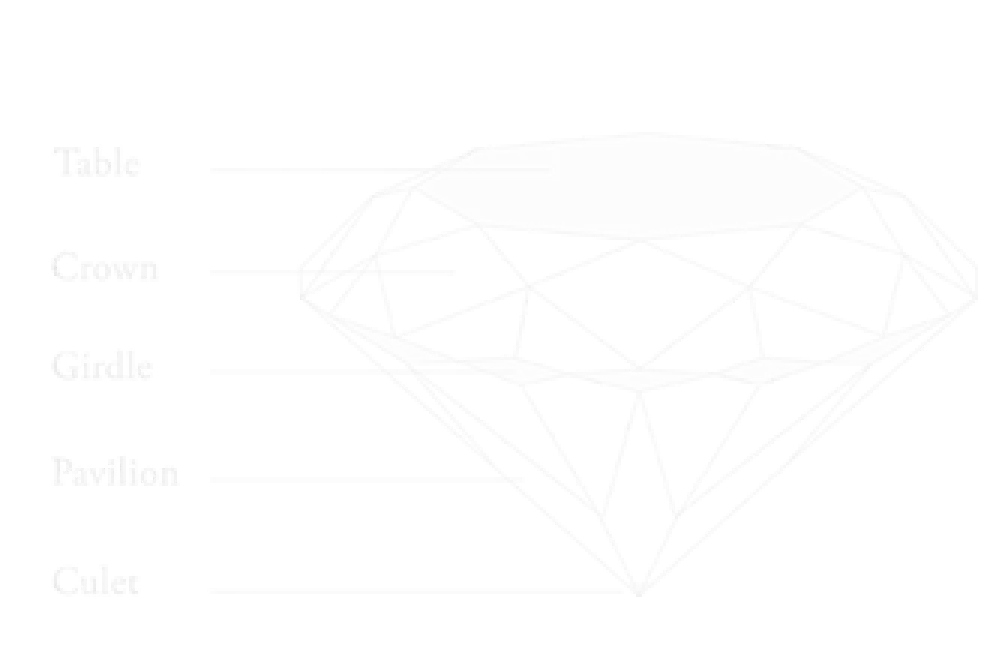
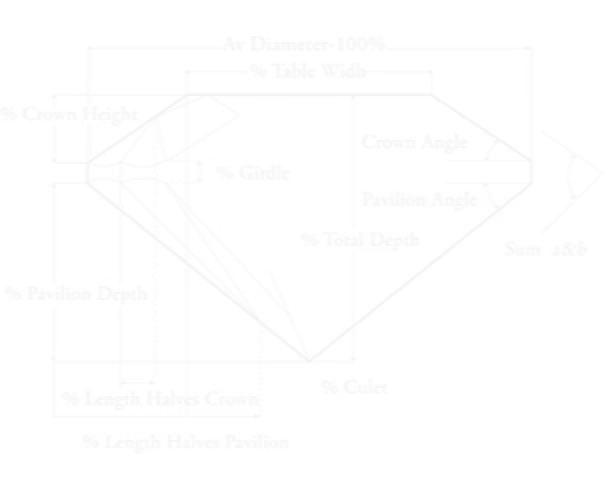
Diamond Anatomy
When buying a diamond, understanding the 4Cs – Cut, Clarity, Colour, and Carat Weight is essential. These key factors determine the diamond’s overall quality, brilliance, and value. Mastering the 4Cs helps you choose the perfect diamond that matches your style and budget.
Table : The Table is the largest polished facet on the top of the diamond. It allows light to enter and reflect, directly affecting the diamond’s brilliance and sparkle. A well-cut Table enhances the diamond’s overall beauty.
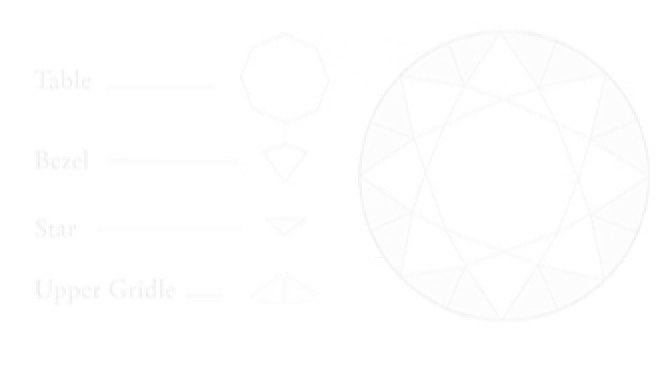
Crown :The Crown is the upper section extending from the Table to the Girdle. It includes Bezel, Star, and Upper Girdle facets that add to the diamond’s fire and scintillation. The Crown greatly influences how the diamond plays with light.
Girdle : The Girdle is the diamond’s widest edge where the Crown meets the Pavilion. It provides strength and protects the stone from damage. The thickness of the Girdle also impacts the diamond’s overall proportions.
Pavilion : The Pavilion is the bottom part of the diamond, stretching from the Girdle to the Culet. It reflects light back through the Table to maximize the diamond’s brilliance. Proper Pavilion depth is crucial for optimal sparkle.
Depth : Depth is the total height of the diamond from the Table to the Culet. Correct Depth proportions ensure the diamond reflects light perfectly, enhancing its brightness and fire. Too much or too little depth can reduce sparkle.
Culet : The Culet is the small or pointed tip at the bottom of the diamond. It helps protect the diamond from chipping. Some diamonds have a pointed Culet, while others have a tiny flat facet for durability.
Proportion – Understanding Brilliance, Dispersion & Scintillation
A well-cut diamond is the key to unlocking exceptional beauty, as it enhances diamond brilliance, dispersion, and scintillation—the three core elements of sparkle. When crafted with precision, a diamond reflects light brilliantly, revealing both intense white flashes and colorful fire. This dynamic interaction of light is known as diamond light performance, which is critical in evaluating a stone’s overall visual appeal. Understanding the difference between brilliance and fire in diamonds helps buyers appreciate how each quality contributes to a diamond’s unique character. In particular, light performance in ideal cut diamonds maximizes both brilliance and sparkle, creating an extraordinary effect. Our guide to light reflection in high-quality diamonds highlights how cut, symmetry, and proportions influence shine. By understanding diamond fire and sparkle effects, you can make a more informed and confident purchase that aligns with both style and value.

Proportion – Understanding Brilliance, Dispersion & Scintillation

Wavy Girdle
An ideal cut diamond features a precisely proportioned diamond girdle that enhances both beauty and durability. Proper diamond girdle alignment with the table ensures maximum light return and structural balance. Our diamond girdle guide for premium cut stones highlights the importance of symmetry in achieving brilliance. Understanding diamond anatomy: ideal girdle shape and positioning is key to selecting a truly exceptional stone.

Crown & Pavilion Misalignment
In a Round Brilliant diamond, the top of the pavilion mains and the bottom points of the bezel facets must meet precisely at the girdle to ensure perfect alignment. When the crown and pavilion are misaligned, it creates an asymmetry flaw that can diminish the diamond’s brilliance and overall appearance. Proper facet alignment is essential to maintain the diamond’s sparkle and value. Buyers should carefully evaluate diamond symmetry to avoid stones with noticeable imperfections.

Extra Facets
Off-Center Culet
Diamond facets and their precise arrangement play a vital role in diamond symmetry, which is a key factor in diamond clarity grading. The role of symmetry in diamond quality becomes especially important for high clarity diamonds, where symmetry precision greatly affects the stone’s brilliance and visual appeal. Proper facet alignment in diamonds ensures optimal light reflection, enhancing both beauty and value. Understanding these aspects helps buyers select superior diamonds with exceptional sparkle.

Off-Center Table
The effects of off-centered diamond tables can significantly impact the overall symmetry and brilliance of a stone. When the table facet is not properly aligned and centered parallel to the diamond girdle, it causes uneven crown angles that reduce light performance. Ensuring the diamond table placement is precise is essential for achieving optimal sparkle and value in high-quality diamonds.

Table & Girdle Not Parallel
The importance of parallel table and girdle in diamond symmetry and cut quality cannot be overstated. When the table and girdle are perfectly aligned, it ensures uniform crown angles that enhance the diamond’s sparkle and brilliance.
Misshapen Face
An ideal-cut diamond features a perfectly symmetrical octagonal table where each diamond facet is precisely aligned and equal in size. Any irregularly shaped facets or misshapen areas can compromise the diamond’s optical precision and reduce its overall brilliance. Ensuring flawless facet symmetry is essential to maintain the diamond’s beauty and maximize its light performance.

Faces Not Pointing Up
The diamond facets and their precise facet arrangement play a vital role in defining the overall quality of a diamond. The importance of facet pointing in diamond quality cannot be overstated, as poorly pointed facets significantly affect the diamond’s appearance and brilliance. Properly identifying diamonds with improper facet shapes helps buyers avoid stones with reduced sparkle and value.

Naturals on Crown and Pavilion
What Is Diamond Polish?
Polish quality in diamonds plays a vital role in enhancing a diamond’s brilliance and overall appearance. When shopping for a diamond, it is essential to choose laboratory certified diamonds to ensure authenticity and reliable polish grading in certified diamonds. Poor polish can cause microscopic polish lines, which negatively impact the effects of poor polish on diamond light performance, reducing the diamond’s sparkle and fire. By understanding these factors, buyers can take advantage of expert tips for selecting diamonds with excellent polish, ensuring they invest in stones with superior finish and maximum brilliance. Prioritizing polish quality helps avoid common flaws and guarantees a dazzling diamond that reflects light beautifully.
What Is Diamond Polish?
GD, GO, G – Good, Very difficult to see under 10X magnification
F, FR, FA – Fair, Noticeable under 10X magnification
PR, PO, P – Poor, Easy to notice under 10x magnification/Visible to the unaided eye
VP, VE – Very Poor, relatively easy to notice with the unaided eye
EX or EP – Extremely Poor, Obvious to see with the unaided eye
When selecting a diamond, it’s crucial to understand how diamond polish affects sparkle and value. While a diamond with a Good polish rating may appear flawless to the naked eye, microscopic abrasions or polish lines can dull its brilliance under magnification. These surface imperfections disrupt light reflection, reducing the diamond’s overall sparkle and value.
On the other hand, poor polish grades, such as Fair or Poor, often result in visible flaws that compromise the stone’s beauty, especially in well-lit environments. Similarly, flaws from mass-produced rings, like porosity in the metal, can impact the ring’s durability and aesthetics. Knowing how diamond polish affects sparkle and value helps buyers make informed decisions, especially when investing in heirloom-quality pieces. A high-quality polish ensures maximum brilliance and showcases the true craftsmanship of the diamond. For luxury jewelry, polish isn’t just a detail—it’s a mark of distinction.

What Is Diamond Polish?
Understanding diamond fluorescence and its visual impact is essential for anyone purchasing a high-quality diamond. Fluorescence refers to the soft glow a diamond emits when exposed to ultraviolet light—a natural reaction seen in some stones. While not all diamonds fluoresce, those that do are graded from faint to very strong based on the intensity of the glow. For some buyers, diamond fluorescence can enhance the stone’s appearance, while in others, it may slightly alter the color in bright light. That’s why understanding diamond fluorescence and its visual impact helps in making a confident, informed jewelry investment.

What are the different types of Fluorescence?
Diamond fluorescence is a fascinating feature that can subtly affect a diamond’s appearance under specific lighting. When exposed to UV light, some diamonds emit a visible glow — this is known as diamond color under UV light. The most common glow is blue fluorescence in diamonds, but rare hues like yellow, green, or white can also occur. The degree of fluorescence in diamonds is assessed through fluorescence grading, which ranges from faint to very strong. Understanding fluorescence grading from faint to very strong is essential when evaluating a diamond’s true visual impact. Whether you’re seeking a unique stone or curious about the science behind glowing diamonds: fluorescence in detail, knowing how UV light interacts with your gem can guide a smarter, more confident purchase
Does Fluorescence affect the Diamond?
Milky or oily diamonds: When fluorescence becomes a concern is a topic every buyer should understand before making a purchase. While fluorescence in diamonds doesn’t always affect quality, in some cases—especially with strong blue fluorescence—a diamond may appear hazy or cloudy under certain lighting. This effect is more common in stones with lower color grades. Understanding milky or oily diamonds: when fluorescence becomes a concern helps ensure you choose a diamond that retains brilliance in all conditions.

Ideal Cut Diamonds
An ideal cut diamond is precisely crafted with proportions and angles designed to optimize light performance. When cut with excellent symmetry and polish, the diamond refracts and reflects light perfectly, producing exceptional brilliance and fire that captivate the eye. The concept of the ideal cut diamond dates back to Marcel Tolkowsky’s pioneering work in the early 1900s, where he analyzed the round brilliant cut diamond and established the mathematical standards for the ideal proportions. Though his model wasn’t perfect, it set the foundation for future innovations. Later, experts like Bruce Harding used advanced technology to refine these guidelines further, developing new models that enhanced the precision of ideal cut diamonds.
Today, these diamonds serve as the benchmark against which all other diamonds are graded. Whether it’s a round brilliant or a princess cut diamond, maintaining the ideal proportions ensures maximum sparkle and visual appeal. By focusing on diamond symmetry and polish, cutters can elevate the stone’s ability to bend light, creating that mesmerizing fire and brilliance every jewelry lover seeks. Understanding how ideal cut diamond proportions maximize fire and sparkle helps buyers appreciate the craftsmanship involved and make informed decisions when selecting a diamond that will truly shine for a lifetime.

Hearts and Arrows Diamond by Sunny Diamonds
An Ideal cut diamond is celebrated for its precise diamond proportions and angles that maximize diamond brilliance and fire, making it the gold standard in gem cutting. Among the most exquisite examples are the Hearts and Arrows diamonds, known for their remarkable diamond optical symmetry and intricate arrow and heart patterns visible under specialized tools. These patterns are a direct result of precision cut diamonds crafted with exceptional care. Understanding what is an ideal cut diamond means appreciating the importance of diamond symmetry ratings in ideal cuts, as these ratings directly impact how light interacts with the stone. The features of Hearts and Arrows diamonds showcase not just technical mastery but also artistic beauty, combining diamond polish, symmetry, and brilliance to create mesmerizing sparkle. These stones set the benchmark standards for ideal cut diamonds, offering unmatched optical performance. Truly, the art of precision cutting in ideal cut diamonds is a blend of science and craftsmanship, resulting in diamonds that captivate the eye and heart alike.

Color & Intensity
The primary colour of the diamond sets the overall hue, such as pink, while the secondary colour of the diamond, like purplish, adds subtle variations that affect the stone’s tone.
Together, these colours define the diamond’s appearance, but the diamond colour intensity—ranging from faint to fancy vivid—ultimately drives its value. As the intensity increases, the diamond’s brilliance and rarity grow, making fancy diamonds with strong hues highly sought after.
Understanding the interplay between primary and secondary diamond colours and their combined impact on tone helps buyers appreciate the nuanced grading system used in fancy diamond grading.
The fancy colour diamonds can be divided as – faint, very light, light, fancy light, fancy intense, fancy vivid/fancy deep/fancy dark.
Fancy Yellow
Fancy Yellow diamonds, also known as Canary Diamonds, stand out distinctly on the diamond colour scale due to their vibrant hues and exceptional rarity. Unlike white diamonds with slight yellow tinges, these stones are classified through a detailed fancy yellow diamond grading system that includes categories such as fancy intense yellow diamond and fancy vivid yellow diamond.
The unique coloration is primarily caused by the presence of nitrogen in diamonds, which gives these gems their unforgettable yellow glow.
As some of the most popular among fancy coloured diamonds, their rare beauty of fancy vivid yellow diamonds commands a higher fancy yellow diamond price, especially when factoring in the fancy yellow diamond carat size. Buyers can explore a variety of fancy yellow diamond styles and carat options to find the perfect match, guided by the precise grading scale for fancy yellow diamonds.
These diamonds, with their captivating brilliance and color depth, make a bold yet elegant choice for anyone seeking something beyond the traditional diamond look.
Fancy Pink
These rare gems, especially the intensely saturated and purplish pink varieties, are highly coveted and often command premium prices. Among the most famous are Argyle Pink Diamonds, known for their vibrant color and scarcity. Understanding this natural coloring process helps collectors and buyers appreciate why fancy pink diamonds are among the most prized and valuable in the world of gemstones.

Fancy Green

Diamond Fluorescence
Fluorescence in diamonds is a fascinating natural effect where a diamond emits a soft color glow of diamond fluorescence when exposed to ultraviolet light fluorescence. This phenomenon varies widely, with types of fluorescence grading in diamonds ranging from faint to very strong fluorescence in diamonds. Understanding diamond fluorescence under UV light explained helps buyers recognize how this glow can influence both the appearance and the impact of fluorescence on diamond value.
What are the different types of Fluorescence?
Does Fluorescence affect the Diamond?
Blue fluorescence in diamonds can subtly influence the look of a yellow colored diamond, often enhancing its brightness. Many buyers ask, does fluorescence affect diamond quality? Generally, diamond quality and fluorescence are independent factors, meaning fluorescence does not reduce a diamond’s value. However, the impact of strong blue fluorescence on diamond clarity can sometimes cause a milky or hazy effect.

Fancy Brown

Fancy orange
A fancy orange diamond is a rare and stunning choice for those seeking something truly unique. These vibrant orange diamonds are graded on a specific grading scale for orange diamonds, including classifications such as fancy intense orange, fancy vivid orange, fancy deep orange, and fancy dark orange.
A true fancy orange diamond with no brown overtone is especially rare, offering exceptional brilliance and purity of color. Some fancy orange diamonds with pink or yellow shades also captivate collectors with their warm, radiant glow. Available in various fancy orange diamond styles and carat sizes, these gems are perfect for those curating orange diamonds for luxury collections.
Whether you’re choosing an engagement ring or a statement piece, natural fancy orange diamond rings offer a bold, elegant alternative to traditional stones.
Diamond Certificate
What is a Diamond Certificate?
A diamond certificate is an official document issued by reputed diamond grading laboratories such as GIA (Gemological Institute of America), AGS (American Gem Society), or HRD Antwerp, which thoroughly assesses a diamond’s quality. It includes the 4Cs of diamonds—Color, Clarity, Cut, and Carat – that together determine its value and beauty. Understanding the 4Cs in diamond grading is essential for any buyer aiming to make an informed purchase.
The importance of diamond certification lies in its ability to assure the authenticity and grade of your gem. When selecting a solitaire, having a diamond certification for solitaires from trusted diamond grading laboratories is crucial for transparency and long-term value. The differences between GIA, AGS, and HRD certificates may influence your buying decision, making it vital to compare them carefully. Always insist on a diamond authenticity certificate to safeguard your investment. So, if you’re wondering what is a diamond certificate, it’s your first step toward confident and secure diamond ownership.
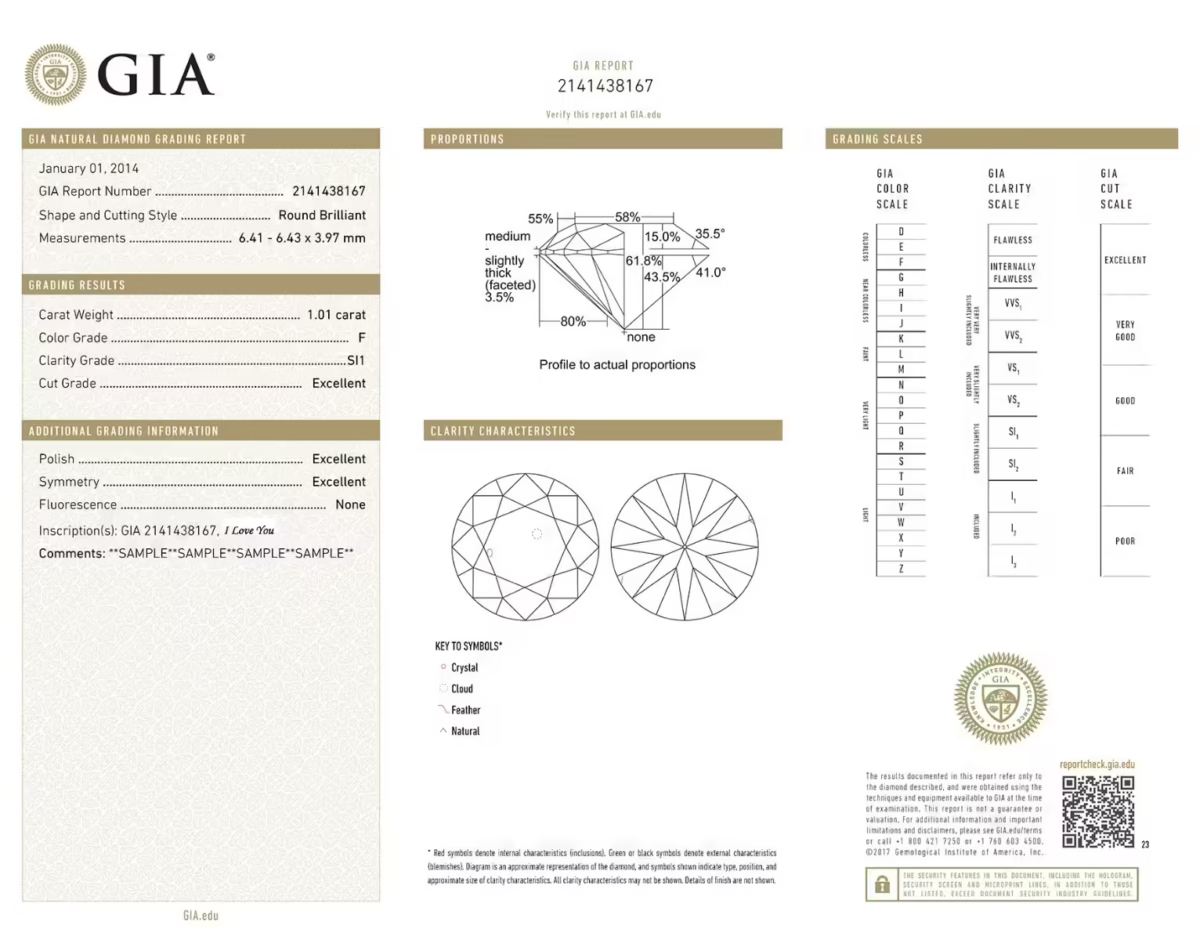
GIA Diamond Certification
The GIA (Gemological Institute of America) plays a crucial role in the world of gemology by setting the benchmark for diamond certification and gemstone evaluation. Established in 1931, GIA introduced its globally recognized diamond grading system in 1953, revolutionizing how diamonds are assessed. The importance of GIA certification lies in its credibility—each GIA certificate is the result of an unbiased gemologist analysis, ensuring accuracy and integrity. Trusted worldwide, GIA’s thorough evaluation of a diamond’s cut, color, clarity, and carat gives buyers confidence and transparency. GIA’s role in gemology has cemented its reputation as the most respected name in the diamond industry, helping customers make informed, secure investments.

AGS Diamond Certification
The American Gem Society (AGS), founded in 1943, is renowned for its commitment to upholding the highest ethical grading standards of the AGS in the diamond industry. When you choose an AGS certificate, you are assured of an independent diamond certification by AGS from one of the most trusted gemological labs for diamonds worldwide. The AGS diamond grading lab uses a precise and ethical diamond grading system to provide accurate diamond evaluation and certification. Their diamond certification reflects rigorous standards that protect buyers and maintain market integrity.
Moreover, the education by American Gem Society ensures that both professionals and consumers understand the importance of quality and authenticity in diamonds. With a focus on transparency and expertise, the American Gem Society diamond grading process remains a benchmark in the industry, offering clarity and confidence to diamond buyers everywhere. Understanding the AGS certificate meaning is essential for anyone investing in certified diamonds.

HRD Diamond Certification
The Hoge Raadvoor Diamant (HRD) is a leading authority in European diamond certification, known for its rigorous HRD diamond certificate that guarantees authenticity and quality.
Based in Antwerp, the HRD plays a crucial role in global diamond trade, overseeing diamond import and export while providing trusted diamond trade monitoring. Consumers highly value the HRD certification value, as it ensures thorough HRD diamond grading and verification by expert gemologists.
Purchasing a certified diamond or certified diamond jewellery with an HRD certificate offers confidence and transparency. Sunny Diamonds proudly offers an extensive HRD certified diamond jewellery collection, emphasizing quality and trust. Moreover, owning an HRD-certified diamond enhances diamond resale value with HRD certification, making it a smart investment for collectors and enthusiasts alike.
Why is a Grading Certificate Not Enough?
A diamond grading certificate is essential, but it doesn’t always reveal a diamond’s complete story. Two 1.01 carat Internally Flawless Excellent Cut Round Diamonds may appear identical on paper, yet differ vastly in real-world brilliance and beauty. That’s where diamond display technology plays a critical role—helping buyers distinguish subtle differences that even a diamond certificate can’t show. While both stones may be graded as Excellent Cut and Internally Flawless, their visual performance, including fire and sparkle, can vary based on proportions and light reflection. Especially in round diamonds, these details impact diamond worth significantly. Understanding the difference between diamonds with the same certificate empowers customers to make informed, confident choices. Always go beyond the certificate and see the diamond for what it truly is.
Example A – 1.01 Carat, I-Colour – Internally Flawless (IF) Excellent Cut Round Diamond
Example B – 1.01 Carat, I-Colour – Internally Flawless (IF) Excellent Cut Round Diamond
Now let us look at the actual diamonds
Example A – 1.01 Carat, I-Colour – Internally Flawless (IF) Excellent Cut Round Diamond
Example B – 1.01 Carat, I-Colour – Internally Flawless (IF) Excellent Cut Round Diamond
When selecting a diamond, relying solely on a diamond grading certificate may not reveal the complete picture of the gem’s beauty. Viewing diamond images allows for a better diamond comparison, especially when evaluating diamond clarity and spotting differences in brilliance. An eye-clean diamond appears flawless to the naked eye, even if minor inclusions exist under magnification. This level of detail is essential for confident diamond selection and ensuring you invest in exceptional diamond quality. Always consider visual inspection alongside certification for a truly informed choice.

Conflict-Free Diamonds
At Primira luxury Diamonds, we pride ourselves on offering only certified conflict-free diamonds from trusted suppliers who strictly adhere to ethical mining practices. Our commitment to providing ethically sourced diamonds with Kimberley Process verification ensures that every stone is free from any association with conflict or exploitation. By working exclusively with members of the professional diamond trade, we guarantee full compliance with international standards and UN guidelines. This rigorous sourcing policy helps buyers confidently select certified conflict-free diamonds that uphold the highest ethical values. Choose Primira luxury Diamonds for transparency, trust, and responsibly sourced luxury jewellery crafted with integrity.

What Are Eye Clean Diamonds?
At Primira Luxury Diamonds, an eye-clean diamond is defined as one without visible diamond inclusions when viewed with the naked eye diamond clarity standard. To ensure this, diamonds are carefully inspected under optimal conditions such as daylight diamond viewing and fluorescent lighting diamond environments. The clarity is assessed from a specific diamond clarity distance, usually between 6 to 12 inches. However, there are three major points to note as you talk about eye-clean diamonds.
1.Distance and point of reference for viewing diamond inclusions (6-12 inches)
2.Lighting conditions during diamond evaluation (daylight and fluorescent lighting)
3.Observer’s eye vision and its impact on clarity assessment
The GIA eye-clean diamonds and AGS eye-clean diamonds grading standards include top clarity grades like Flawless diamonds (FL), Internally Flawless diamonds (IF), and Very Very Slightly Included diamonds (VVS1, VVS2). Diamonds graded as Very Slightly Included (VS1, VS2) may also be considered eye-clean, while Slightly Included diamonds (SI1, SI2) could vary in clarity visibility. However, Included diamonds (I1, I2, I3) are not classified as eye-clean due to noticeable inclusions. Understanding these classifications helps buyers make informed decisions about diamond quality.
How to Choose the Perfect Diamond
When purchasing a classic diamond, understanding the key diamond characteristics is essential to find the perfect diamond. The 4Cs of diamonds—Cut, Clarity, Colour, and Carat weight—play a crucial role in determining a diamond’s value and beauty. Our comprehensive diamond buying guide helps you navigate these important factors, ensuring you make an informed decision when purchasing a diamond. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or a seasoned collector, mastering the 4Cs will lead you to the ideal stone that fits your style and budget.
The 4 C's:
When purchasing a diamond, understanding key aspects like diamond cut, ideal cut diamond, diamond clarity, diamond colour, diamond carat, and diamond shape is essential to find the perfect stone. The diamond anatomy and diamond grading play a crucial role in evaluating the overall quality, including factors such as diamond brilliance, diamond fire and scintillation, and the proportion and polish in diamond cut. Among cuts, hearts and arrows precision cut diamonds stand out due to their exceptional symmetry and light performance, enhancing the diamond’s brilliance and fire.
Knowing the diamond clarity grades and inclusions helps in assessing purity, where flawless stones are highly prized, but diamonds with minor inclusions can still be valuable if they are not visible to the naked eye.
The colour scale of diamonds from D to Z guides buyers on hue, with the best diamond colours for value (J, K, L) offering an excellent balance between quality and price. Understanding diamond carat weight and pricing is key, as carat size impacts the diamond’s cost, but it must be considered alongside other 4Cs to select the ideal stone.
Exploring various diamond shapes for purchase, such as round, princess, cushion, emerald, marquise, and more, allows customization to personal taste. Understanding diamond anatomy for buying, including brilliance, dispersion, and scintillation, gives deeper insight into a diamond’s beauty.
Learning how to choose the perfect diamond for budget and preference ensures satisfaction, balancing size, clarity, and colour to find a stone that fits individual style. The carat weight explained: impact on diamond pricing further clarifies how weight affects cost, while popular diamond shapes available for custom jewellery provide flexibility for unique designs.
Focusing on key factors in diamond anatomy: brilliance, dispersion, scintillation, helps buyers appreciate what makes a diamond truly exceptional. Ultimately, personalized diamond selection based on budget and style allows customers to invest wisely in stones that combine beauty and value.
Understanding the characteristics of ideal cut diamonds with excellent symmetry and the precision hearts and arrows diamond cut benefits elevates the buying experience, ensuring you choose a diamond with unmatched sparkle and quality. This comprehensive knowledge enables confident diamond purchases that reflect both personal taste and long-term value, making your investment in fine jewellery rewarding and fulfilling.

Diamond Care
Proper diamond cleaning and diamond maintenance are essential to keep your precious jewelry sparkling and looking its best. Whether it’s a wedding ring cleaning, engagement ring cleaning, or general diamond care, using safe cleaning methods for diamond rings is crucial to avoid damage.
The best way to clean engagement rings safely often involves gentle techniques such as cleaning diamond ring with mild soap and using a soft toothbrush to clean diamond surfaces carefully. Many jewelry owners benefit from easy DIY diamond ring cleaning tips at home, following a step-by-step guide to safely clean your diamond ring without risking scratches or harm.
One important tip is to avoid scratching diamond with paper towels, which can damage the metal or stone. Instead, use a soft cotton cloth for drying. It’s also important to know how to remove dirt from diamond prongs and how to remove dirt buildup around diamond prongs gently without scratching or loosening the stone. While ionic diamond cleaners are popular, be aware of ionic diamond cleaners warnings, especially if your ring contains gemstones other than diamonds, as these devices can have adverse effects.
Following best household methods to clean engagement rings without damage and safe and effective diamond ring cleaning without harsh chemicals will ensure longevity and brilliance. Many people wonder how to maintain diamond shine using gentle cleaning solutions, and the answer lies in regular, careful cleaning and avoiding common diamond cleaning mistakes to prevent scratches.
Always protect your diamond ring from scratches while cleaning by keeping it separate from other jewelry, as diamonds can only be scratched by other diamonds. For those seeking a comprehensive routine, learning how to clean your wedding ring using mild soap and soft brushes can transform your jewelry care and keep your diamond dazzling for years to come








